Advancements in Treating Estrogen Positive Breast Cancer Effectively
Estrogen positive breast cancer presents unique challenges and opportunities for treatment. With modern medical advancements, there is a deeper understanding of hormonal therapies and treatments. This exploration of the latest treatment options offers hope and guidance to those impacted by this type of breast cancer.
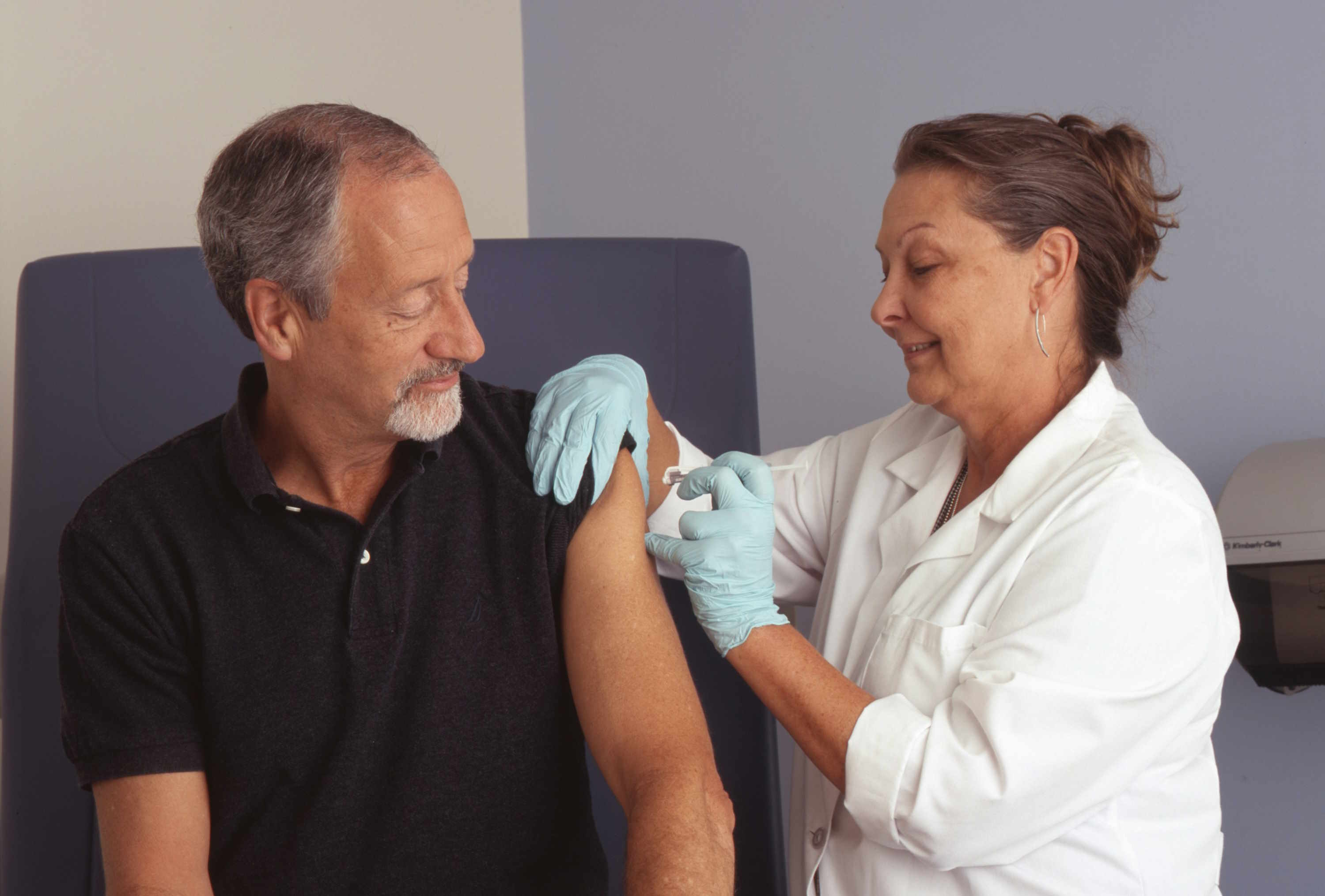
What is estrogen positive breast cancer?
Estrogen positive breast cancer, also known as ER-positive breast cancer, is characterized by the presence of estrogen receptors on cancer cells. These receptors allow the cancer to respond to estrogen, which can promote tumor growth. Understanding this fundamental aspect is crucial for developing targeted treatments. The identification of ER-positive breast cancer is typically done through hormone receptor tests, which analyze tissue samples to determine the presence and concentration of these receptors [1].
How does hormonal therapy work in treating ER-positive breast cancer?
Hormonal therapy, also called endocrine therapy, is a cornerstone in treating estrogen positive breast cancer. It works by either lowering estrogen levels in the body or blocking estrogen from attaching to cancer cells. This approach effectively starves the cancer of the hormones it needs to grow and spread. There are several types of hormonal therapies available, including selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), aromatase inhibitors, and estrogen receptor downregulators [1].
What are the latest advancements in hormonal therapy?
Recent advancements in hormonal therapy have focused on improving efficacy and reducing side effects. One significant development is the introduction of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibitors. These drugs, when combined with traditional hormonal therapies, have shown remarkable success in slowing cancer progression and improving survival rates in metastatic ER-positive breast cancer patients. Additionally, extended adjuvant therapy, where hormonal treatment is continued for up to 10 years after initial treatment, has demonstrated improved long-term outcomes for many patients [1].
How does ovarian suppression contribute to breast cancer treatment?
Ovarian suppression is a critical component of treatment for premenopausal women with ER-positive breast cancer. This approach aims to reduce estrogen production by the ovaries, either through medication or surgical removal of the ovaries. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists are commonly used drugs that temporarily shut down ovarian function. Studies have shown that combining ovarian suppression with other hormonal therapies can significantly improve outcomes in younger women with high-risk ER-positive breast cancer [1].
What role do targeted therapies play in ER-positive breast cancer treatment?
Targeted therapies have revolutionized the treatment landscape for ER-positive breast cancer. These therapies are designed to attack specific features of cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy cells. PI3K inhibitors, for instance, target a specific pathway often overactive in ER-positive breast cancers that have become resistant to hormonal therapies. Another promising area is the use of immunotherapies in combination with hormonal treatments, which has shown potential in enhancing the body’s immune response against cancer cells.
How are personalized treatment plans developed for patients?
Developing personalized treatment plans for ER-positive breast cancer patients involves a comprehensive approach that considers multiple factors. Genetic testing, such as Oncotype DX or MammaPrint, helps predict the likelihood of cancer recurrence and the potential benefit of chemotherapy. This information, combined with factors like tumor size, grade, and lymph node involvement, guides decisions on treatment intensity. Additionally, lifestyle factors and patient preferences are taken into account to create a tailored treatment strategy that balances efficacy with quality of life considerations.
What are the costs associated with ER-positive breast cancer treatment?
The cost of treating ER-positive breast cancer can vary significantly based on the specific treatments required, duration of therapy, and individual healthcare coverage. Here’s a general overview of potential costs associated with common treatments:
| Treatment Type | Provider | Estimated Cost Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Hormonal Therapy (annual) | Various Pharmaceutical Companies | $1,000 - $15,000 |
| CDK4/6 Inhibitors (monthly) | Pfizer, Novartis, Eli Lilly | $10,000 - $15,000 |
| Ovarian Suppression (annual) | Various Healthcare Providers | $3,000 - $7,000 |
| Targeted Therapies (monthly) | Various Pharmaceutical Companies | $5,000 - $20,000 |
| Genetic Testing (one-time) | Genomic Health, Agendia | $3,000 - $5,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Advancements in treating estrogen positive breast cancer have significantly improved patient outcomes and quality of life. From refined hormonal therapies to innovative targeted treatments and personalized approaches, the field continues to evolve rapidly. As research progresses, we can expect even more effective and tailored treatment options for individuals facing ER-positive breast cancer, offering hope for better long-term survival and improved quality of life.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
The shared information of this article is up-to-date as of the publishing date. For more up-to-date information, please conduct your own research.
Sources: 1. https://www.komen.org/breast-cancer/treatment/type/hormone-therapy/